downward displacement autoclave|gravity vs liquid cycle autoclave : manufacture It is very important to ensure that all of the trapped air is removed from the autoclave before activation, as trapped air is a very poor medium for achieving sterility. Steam at 134 °C (273 °F) can achieve a desired level of sterility in three minutes, while achieving the same level of sterility in hot air requires two hours at 160 °C (320 °F). Methods of air removal include: Downward displacement (or gravity-type): As steam enters the chamber, it fills the upper areas f. Step 1: To prepare 100 ml of 1M Glucose solution, weigh out 18 g Glucose in a 250 conical flask/beaker. Add 80 ml deionized/Milli-Q water. Stir until all glucose is . See more
{plog:ftitle_list}
Prepare 50% glycerol solution in a 250 ml bottle. Add equal volumes of 100% glycerol and dI H2O. Mix well to distribute the viscous glycerol solution. Using a serological pipet or the P1000 multichannel, add the volume listed below to .
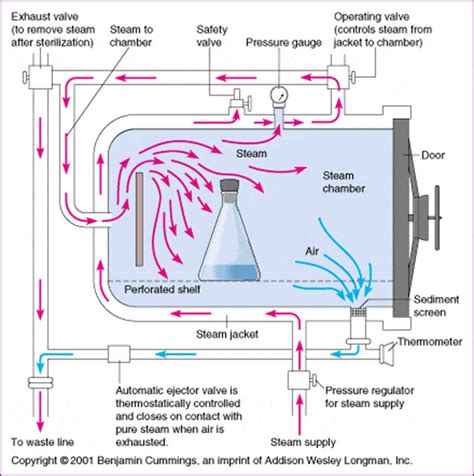
In gravity autoclaves or gravity displacement / downward displacement autoclaves, the pressurized steam does the work of pushing out and replacing the ambient air until the chamber is saturated with steam.It is very important to ensure that all of the trapped air is removed from the autoclave before activation, as trapped air is a very poor medium for achieving sterility. Steam at 134 °C (273 °F) can achieve a desired level of sterility in three minutes, while achieving the same level of sterility in hot air requires two hours at 160 °C (320 °F). Methods of air removal include: Downward displacement (or gravity-type): As steam enters the chamber, it fills the upper areas f.Using a laboratory downward displacement vertical autoclave with the help of thermocouples recorded on a 12 point multichannel strip recorder, the risk of failing to sterilize laboratory discard buckets has been demonstrated. The use of proper temperature and .Our autoclaves are downward displacement models. They work by forcing steam in at the side or back of the chamber which displaces the air downwards and out through a grated drain. There is turbulence inside the chamber (the steam comes in at about 25 p.s.i.) but solid walled trays can create a tub of air which prevents steam from contacting the .
Abstract— An Autoclave or a steam sterilizer is an important vehicle for reducing the microbial contamination of packaged final products, . 2.2.1 Downward displacement (or gravity-type) Cycles: As steam enters the chamber, it fills the upper areas first as it is less

The 433HC-E and 533HC-E Series offer cycles employing either gravity/downward displacement or pressure/vacuum pulsing. The sterilizers offer up to 24 cycles in two easy steps for applications including wrapped and unwrapped porous and non-porous hard goods, utensils, gowns or towel packs and liquids in self-venting or unsealed containers. Image 3: Vertical construction of autoclave with labelled image Types of Autoclaves There are 02 types of autoclave systems commercially available: Gravity displacement. In this type of Autoclave, the steam is produced when the water is boiled, then the steam produced replaces the air by gravity. Horizontal (comes in horizontal shape)
There are two types of autoclaves, namely, upward displacement autoclaves and downward displacement autoclaves, based on their technique of air removal. A pressure cooker is a basic example of an upward displacement autoclave, in which the steam is produced by boiling water with the help of heaters placed at the bottom of the vessels.Every Priorclave autoclave comes standard with our advanced fully programmable control system, Biomaster® protected antimicrobial surface coatings, free lifetime technical support, and a low-energy/low-water easy-maintenance design optimised to minimise lifetime operating costs.The first is steam purging, also sometimes known as downward displacement air removal. This is normally a timed sequence, so that as the autoclave admits/raises steam and heats above 80°C, a small exhaust valve opens, and it effectively pushes the air from the chamber. Our Touchclave-R autoclaves use this method as standard. As this method is .Using a laboratory downward displacement vertical autoclave with the help of thermocouples recorded on a 12 point multichannel strip recorder, the risk of failing to sterilize laboratory discard buckets has been demonstrated. The use of proper temperature and time controls can prevent this risk. A load in a bucket with perforated sides is more .
what is gravity displacement sterilization
Tests at 27 laboratories, mostly PHLS, on 46 downward displacement autoclaves showed that the sterilizing performance was unsatisfactory on 10 of 62 occasions. The results of this survey together with advisory notes on the safe and efficient use of laboratory autoclaves have been published (PHLS Subcommittee on Laboratory Autoclaves, 1978). The downward displacement autoclave is also referred to as a gravity displacement unit. This is because of the method of air removal in the sterilization chamber. A heating element is submerged in a pool of water, which, when heated, becomes steam. As steam is lighter than air, it forces the air in the sterilization chamber downward and out .The 700HC-E Series offer cycles employing either gravity/downward displacement or dynamic air-removal pressure/vacuum pulsing. Offering up to 23 cycles, in two easy steps for applications including wrapped and unwrapped porous and non-porous hard goods, utensils, gowns or towel packs and liquids in self-venting or unsealed containers.
Benchtop steam sterilisers (autoclaves) . Gravity (downward displacement) sterilisers are the easiest to monitor and the most cost-efficient. Table 10.6. Steriliser types. Type. Class. Description. Example of temperature -pressure curve. Gravity (downward displacement) and active drying. N. Autoclave - Download as a PDF or view online for free. . Two main types are discussed: downward displacement and vacuum. Proper use requires loading, pressurizing to 15 PSI and heating to 121 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes to effectively kill microbes. Autoclaves provide rapid and effective sterilization but items must be heat tolerant and .This reduces both scheduled and unscheduled maintenance, and makes service calls quicker, less disruptive, and less expensive. Priorclave drives down the total operating cost for its horizontal autoclaves by minimizing maintenance, . An autoclave is a piece of equipment used to sterilize objects using high-pressure steam. Many fields and industries utilize autoclaves, including medicine, tattoo parlors, dentistry, and most .
Autoclave is the most common method of sterilization in the laboratory working on moist heat. Sterilization is the process of removing or. Skip to content. . large simple autoclaves, downward displacement laboratory autoclaves, media preparatory autoclaves, and multi-purpose laboratory autoclave.
‘Autoclave’ is a term used mainly in laboratories whilst ‘Sterilizer’ is used more commonly for medical and pharmaceutical applications. In simple terms, . (downward displacement) with the vent only closing when all of the air is removed from the chamber. This method can be further advanced by ‘Freesteaming’ when the vent is .
Gravity autoclaves (also known as “gravity displacement autoclaves”) are the most common types of steam sterilizers available on the market. While they are less sophisticated than vacuum autoclaves, that doesn’t mean they are not a viable solution for certain medical facilities. . and cooled down in about 20 minutes. Extra safety .Using a laboratory downward displacement vertical autoclave with the help of thermocouples recorded on a 12 point multichannel strip recorder, the risk of failing to sterilize laboratory discard buckets has been demonstrated. The use of proper temperature and .
youtube column chromatography pasteur pipette
'upward' displacement, or an external supply (i.e. steam generator on in-house steam) resulting in 'downward displacement'. This purging process (also known as 'freesteaming') can be programmed to continue for a set length of time. The turbulent steam passes through the vent, forcing trapped air out of the autoclave. Once the airUsing a laboratory downward displacement vertical autoclave with the help of thermocouples recorded on a 12 point multichannel strip recorder, the risk of failing to sterilize laboratory discard buckets has been demonstrated. The use of proper temperature and .Autoclave is medical equipment that was initially created by a French microbiologist Charles Chamberlain in 1879. . A download displacement device or a gravity displacement unit. It was called so due to the method of the air removal in a special sterilization chamber. . when the steam enters it from a downward displacement (external supply .
youtube how to use a pipette
In a Downward Displacement Autoclave, also known as a horizontal or gravity displacement unit, cold air escapes through the bottom of the chamber as steam displaces it from above. This type of sterilizer uses a heating elements to heat up the water and produce steam. The steam then forces the air inside the sterilization chamber to move .An autoclave is a heated chamber used to sterilize various types of media, by means of dry saturated steam under pressure. . In this scenario, air is allowed to vent the chamber as steam enters from either an integral source (upward displacement) or from an external supply (downward displacement). Downward displacement (DD) For these experiments the large-bore valve was closed from the beginning of the cycle, reliance for air and condensate removal being placed on the near- to-steam trap fitted in the chamber drain line. . Sterilisation in the laboratory autoclave using direct air displacement by steam. Journal of Clinical Pathology 31 .
These sterilizers use a process called gravity displacement, which gradually pushes the air out of the autoclave’s chamber. Air is one of the greatest obstacles for efficient sterilization, and without the vacuum pump used by more advanced models, this process is slower, but also cannot remove 100% of the air inside.
prevac vs gravity sterilization
pre vacuum vs gravity autoclave
At 121°C, the time of autoclaving to achieve sterilization is generally considered to be 15-20 min, depending on the volume of the load. To make sure, sterilization is successful one should ensure: Air should be evacuated so that .
downward displacement autoclave|gravity vs liquid cycle autoclave